
The circuit in the original question contains 1 or more hazards or race conditions. There are 4 stable states and 12 states that are transistional between stable states in normal operation. I will provide this information, but not as a diagram. For example, the OPs circuit, shows up all over the place labeled as a T flip-flop despite the fact that it has problems described in other answers.) However, I am offering the above information as an alternative point of view to that of the commenter.Įdit2: A commenter has asked for a state diagram for the circuit. (There is certainly a lot of misinformation about flip-flops on the interwebs. I don't claim that this is necessarily an authoritative refutation of the claim that a T flip-flop must have separate T and clock inputs. It can be made from a J-K flip-flop by tying both of its inputs high. It is useful for constructing binary counters, frequency dividers, and general binary addition devices. The T or "toggle" flip-flop changes its output on each clock edge, giving an output which is half the frequency of the signal to the T input.

However, when I google "T flip-flop", the very first hit that comes up for me is this which states: Someone has commented that this circuit is not a T flip-flop because the circuit depends upon the clock alone, and does not have separate T and clock inputs. Simulate this circuit – Schematic created using CircuitLab The circuit below simulates fine in CircuitLab. Unlike the Master-Slave design, which needs a complete pulse, you can also build an edge-triggered design that triggers from a rising edge ↑ or a falling edge ↓.To implement an edge triggered T Flip-Flop that does not rely on gate delay timing, requires, I believe, a minimum of 6 Nand gates. That’s why this configuration is called pulse-triggered JK Flip-Flop. So this circuit requires a complete pulse (0→1 →0) in order to change the output. Once the clock signal produces a falling edge ↓, a change from 1 to 0 (1→0), it triggers the slave section, causing the Q output to reflect the master’s output value. These signals are connected to the slave section, but this doesn’t trigger on the rising edge because the clock has been inverted. As a result, the value of the outputs in this section changes.
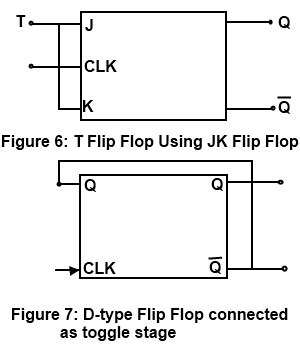
As soon as the clock makes a rising edge ↑, which is a change from 0 to 1 (0→1), it triggers the master section.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
